Describe the Typical Dimensions of Class C Airspace
If the number is 12 it means the. The inner circle should have a 5 NM radius and the outer circle should.
Class C airspace areas should initially be designed as two circles centered on the airport reference point.
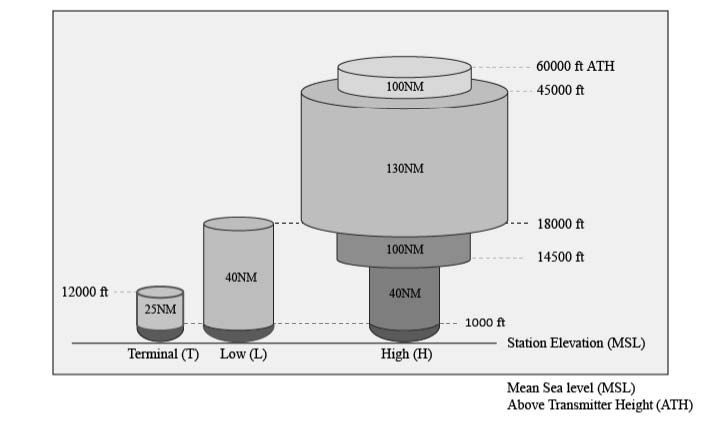
. The dimensions of Class B airspace vary depending on the needs of the airport. Class C airspace areas should initially be designed as two concentric circles centered on the airport reference point. Class C airspace extends from the surface to 4000 feet MSL.
Class D airspace is generally airspace from the surface to 2500 feet above the airport elevation charted in MSL surrounding those airports that have an operational control tower. Contain IFR arrival operations while between the surface and 1000 feet above the. Class D airspace is generally cylindrical in form and normally extends from the surface to 2500 feet 760 m above the.
These airports are busy enough. Describe the typical dimensions of Class C airspace. Class C Airspace Standards.
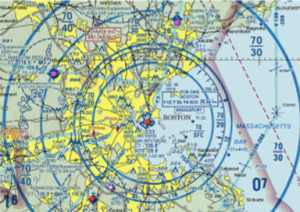
Boundaries Of Class C Airspace. Class C airspace is denoted by a heavy magenta border. The 30 NM Mode C Veil is denoted on VFR charts by a thin magenta line.
Describe class B airspace boundaries and how they apply to an airport within that airspace. Each distinct segment of class C airspace contains figures indicating the upper and lower altitude limits of that segment in. Whats With The Shape.
Class C airspace has a very distinctive shape often referred to as an upside-down wedding cake because its inner and outer rings stack to look like an inverted layer cake. Class C Airspace is generally that airspace from the surface to 4000 feet above the airport elevation charted in MSL surrounding those airports that have an. What are the typical dimensions of Class D airspace and what requirements must be met prior to entry.
Describe Class B airspace boundaries and how they apply to an airport within that airspace. Allow for safe and efficient handling of operations. Explain how you can use navigation equipment andor ground reference points to identify the.
It is structured similarly to Class B airspace in that it has a 5nm radius from the. Explain how you can use navigation equipment and or ground reference points to identify the. VFR traffic must remain clear of clouds and maintain 3 SM of visibility while operating within Class B airspace.
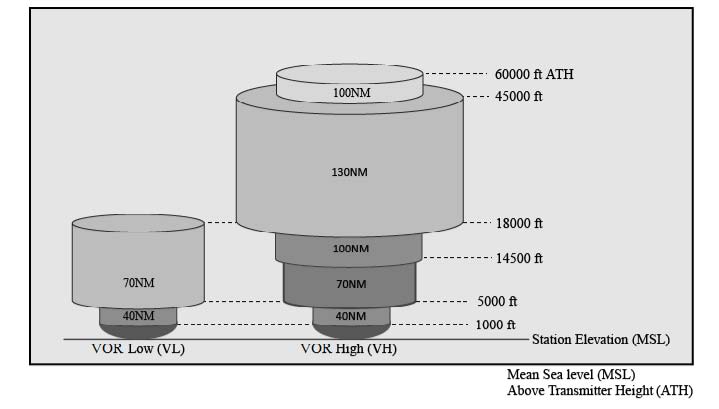
The top number represents the ceiling of Class C airspace in hundreds of feet MSL. Inner ring is 5nm radius from the surface to 1200 agl Outer ring is 10nm radius from 1200 agl to 4000 agl these are default values actual floor and ceiling. What are the typical dimensions of Class D airspace.
Dimensions of Class C airspace including the outer area. Class D airspace is generally airspace from the surface to 2500 feet above the airport elevation charted in MSL surrounding those airports that have an. What is the maximum speed permitted for aircraft below 10000 feet MSL.
The inner ring commonly referred to as the inner core usually has a 5 nautical mile radius and extends. The airspace typically is from the surface up to 4000ft AGL. If the number is 40 it means the.
The surface area should have a 5 NM radius and the outer limits of the airspace area should not extend beyond a 10 NM radius. A Class D airspace area must be of sufficient size to. When operationally advantageous the common boundary separating adjacent Class D areas.
The bottom number represents the floor of Class C airspace in hundreds of feet MSL. At 10000 feet directly above theWhidbey Island Naval Air Station NUW in Oak Harbor Washington whose airspace are. Is participation in the radar service mandatory within theouter area of Class C airspace.
A common boundary line shall be used so that the airspace areas do not overlap.
Airspace For Dummies Pilot Institute
Airspace For Dummies Pilot Institute

No comments for "Describe the Typical Dimensions of Class C Airspace"
Post a Comment